- Infos im HLRS Wiki sind nicht rechtsverbindlich und ohne Gewähr -
- Information contained in the HLRS Wiki is not legally binding and HLRS is not responsible for any damages that might result from its use -
Powersched(Hawk): Difference between revisions
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
==== Powersched ==== | ==== Powersched ==== | ||
Powersched proposes a reliable, efficient, and transparent mechanism to keep a HPC system under a power cap. The tool aims to increase the energy efficiency of available resources by enabling power capping based on an application-specific, energy-optimized runtime environment. The power capping is governed by the GSS | Powersched (HPE) proposes a reliable, efficient, and transparent mechanism to keep a HPC system under a power cap. The tool aims to increase the energy efficiency of available resources by enabling power capping based on an application-specific, energy-optimized runtime environment. The power capping is governed by the Golden-Section-Search (GSS) optimization of a given metric (a variant of the Energy-Delay-Product) and will adapt to different application phases. Depending on the job characteristic we aim for an improvement in energy efficiency of order 20% with a moderate performance impact (or gain) of order 5%. | ||
A summary is included below. | A summary is included below. | ||
==== Golden Section Search (GSS) ==== | |||
[[File:GSS.png|765px]] | [[File:GSS.png|765px]] | ||
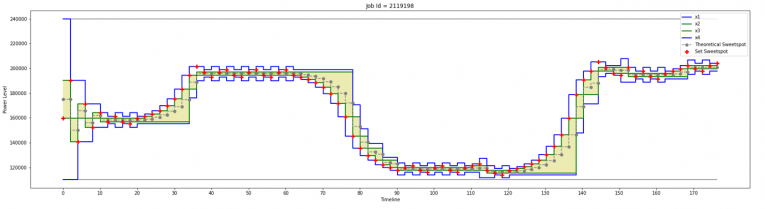
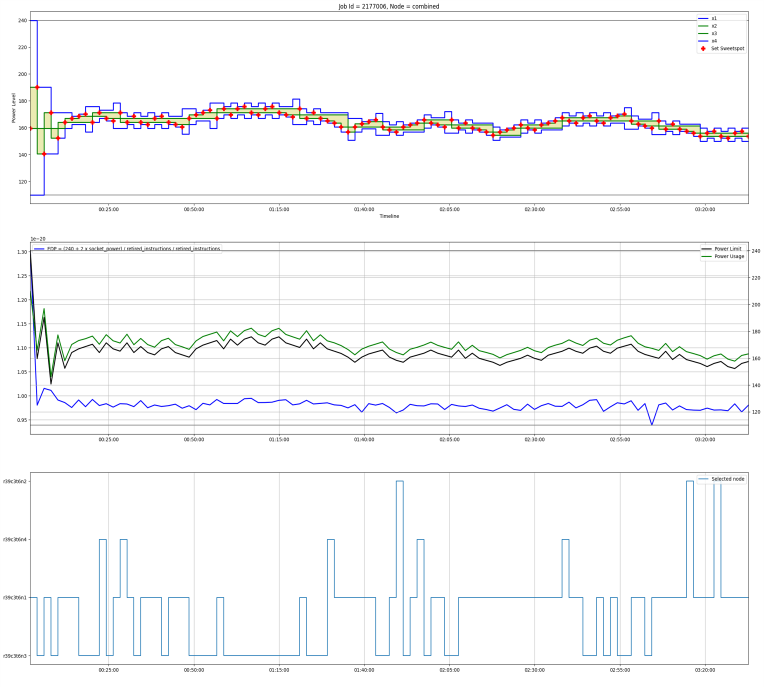
Dynamic power capping (per socket). As a corollary you might observe a relaxation | Dynamic power capping (per socket). As a corollary you might observe a relaxation period especially during startup | ||
and in changing application phases. | and in changing application phases. | ||
Latest revision as of 09:29, 16 January 2024
Power Management (Powersched)
Powersched
Powersched (HPE) proposes a reliable, efficient, and transparent mechanism to keep a HPC system under a power cap. The tool aims to increase the energy efficiency of available resources by enabling power capping based on an application-specific, energy-optimized runtime environment. The power capping is governed by the Golden-Section-Search (GSS) optimization of a given metric (a variant of the Energy-Delay-Product) and will adapt to different application phases. Depending on the job characteristic we aim for an improvement in energy efficiency of order 20% with a moderate performance impact (or gain) of order 5%.
A summary is included below.
Golden Section Search (GSS)
Dynamic power capping (per socket). As a corollary you might observe a relaxation period especially during startup and in changing application phases.